Astrocytes eat connections to maintain plasticity in adult brains
by The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
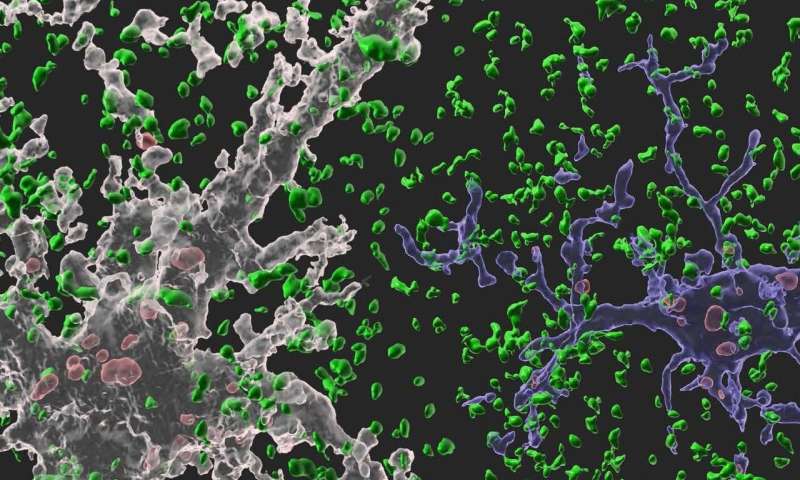
Developing brains constantly sprout new neuronal connections called synapses as they learn and remember. Important connections—the ones that are repeatedly introduced, such as how to avoid danger—are nurtured and reinforced, while connections deemed unnecessary are pruned away. Adult brains undergo similar pruning, but it was unclear how or why synapses in the adult brain get eliminated.
Now, a team of KAIST researchers has found the mechanism underlying plasticity and, potentially, neurological disorders in adult brains. They published their findings on December 23 in Nature.
"Our findings have profound implications for our understanding of how neural circuits change during learning and memory, as well as in diseases," said paper author Won-Suk Chung, an assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. "Changes in synapse number have strong association with the prevalence of various neurological disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, frontotemporal dementia, and several forms of seizures."
Gray matter in the brain contains microglia and astrocytes, two complementary cells that, among other things, support neurons and synapses. Microglial are a frontline immunity defense, responsible for eating pathogens and dead cells, and astrocytes are star-shaped cells that help structure the brain and maintain homeostasis by helping to control signaling between neurons. According to Professor Chung, it is generally thought that microglial eat synapses as part of its clean-up effort in a process known as phagocytosis.
"Using novel tools, we show that, for the first time, it is astrocytes and not microglia that constantly eliminate excessive and unnecessary adult excitatory synaptic connections in response to neuronal activity," Professor Chung said. "Our paper challenges the general consensus in this field that microglia are the primary synapse phagocytes that control synapse numbers in the brain."
Professor Chung and his team developed a molecular sensor to detect synapse elimination by glial cells and quantified how often and by which type of cell synapses were eliminated. They also deployed it in a mouse model without MEGF10, the gene that allows astrocytes to eliminate synapses. Adult animals with this defective astrocytic phagocytosis had unusually increased excitatory synapse numbers in the hippocampus. Through a collaboration with Dr. Hyungju Park at KBRI, they showed that these increased excitatory synapses are functionally impaired, which cause defective learning and memory formation in MEGF10 deleted animals.
"Through this process, we show that, at least in the adult hippocampal CA1 region, astrocytes are the major player in eliminating synapses, and this astrocytic function is essential for controlling synapse number and plasticity," Chung said.
Professor Chung noted that researchers are only beginning to understand how synapse elimination affects maturation and homeostasis in the brain. In his group's preliminary data in other brain regions, it appears that each region has different rates of synaptic elimination by astrocytes. They suspect a variety of internal and external factors are influencing how astrocytes modulate each regional circuit, and plan to elucidate these variables.
"Our long-term goal is understanding how astrocyte-mediated synapse turnover affects the initiation and progression of various neurological disorders," Professor Chung said. "It is intriguing to postulate that modulating astrocytic phagocytosis to restore synaptic connectivity may be a novel strategy in treating various brain disorders."
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/12/201224090406.htm
https://sciencecodex.com/astrocytes-eat-connections-maintain-plasticity-adult-brains-664004
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2020-12-astrocytes-plasticity-adult-brains.html
https://www.miragenews.com/astrocytes-eat-connections-to-maintain-plasticity-in-adult-brains/








