Gut hormone triggers craving for more proteins
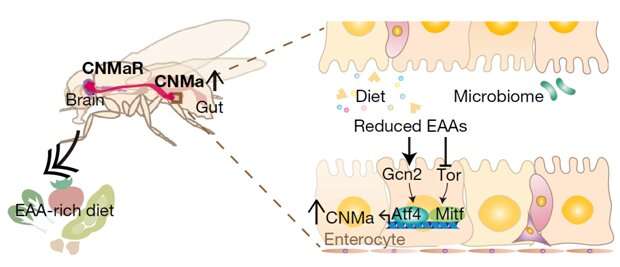
A new study led by KAIST researchers using fruit flies reveals how protein deficiency in the diet triggers cross talk between the gut and brain to induce a desire to eat foods rich in proteins or essential amino acids. This finding reported in the May 5 issue of Nature can lead to a better understanding of malnutrition in humans.
"All organisms require a balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats for their well being," explained KAIST neuroscientist and professor Greg Seong-Bae Suh. "Taking in sufficient calories alone won't do the job, as it can still lead to severe forms of malnutrition including kwashiorkor, if the diet does not include enough proteins," he added.
Scientists already knew that inadequate protein intake in organisms causes a preferential choice of foods rich in proteins or essential amino acids but they didn't know precisely how this happens. A group of researchers led by Professor Suh at KAIST and Professor Won-Jae Lee at Seoul National University (SNU) investigated this process in flies by examining the effects of different genes on food preference following protein deprivation.
The group found that protein deprivation triggered the release of a gut hormone called neuropeptide CNMamide (CNMa) from a specific population of enterocytes—the intestine lining cells. Until now, scientists have known that enterocytes release digestive enzymes into the intestine to help digest and absorb nutrients in the gut. "Our study showed that enterocytes have a more complex role than we previously thought," said Professor Suh.
Enterocytes respond to protein deprivation by releasing CNMa that conveys the nutrient status in the gut to the CNMa receptors on nerve cells in the brain. This then triggers a desire to eat foods containing essential amino acids.
Interestingly, the KAIST-SNU team also found that the microbiome -Acetobacterbacteria—present in the gut produces amino acids that can compensate for mild protein deficit in the diet. This basal level of amino acids provided by the microbiome modifies CNMa release and tempers the flies' compensatory desire to ingest more proteins.
The research team was able to further clarify two signaling pathways that respond to protein loss from the diet and ultimately produce the CNMa hormone in these specific enterocytes.
The team said that further studies are still needed to understand how CNMa communicates with its receptors in the brain, and whether this happens by directly activating nerve cells that link the gut to the brain or by indirectly activating the brain through blood circulation. Their research could provide insights into the understanding of similar process in mammals including humans.
"We chose to investigate a simple organism, the fly, which would make it easier for us to identify and characterize key nutrient sensors. Because all organisms have cravings for needed nutrients, the nutrient sensors and their pathways we identified in flies would also be relevant to those in mammals. We believe that this research will greatly advance our understanding of the causes of metabolic disease and eating-related disorders," Professor Suh added.
https://phys.org/news/2021-05-gut-hormone-triggers-craving-proteins.html
https://www.sciencecodex.com/gut-hormone-triggers-craving-more-proteins-673523
https://www.miragenews.com/gut-hormone-triggers-craving-for-more-proteins-561159/








